You’ve sent emails, but do you know the tech magic behind them? In this article, we’ll explore everything about SMTP and MIME – how SMTP transfers emails, delve into the role of MIME, and even touch on the security of SMTPS.
Table of Contents
If you’re ready to navigate the complex landscape of email communication, SMTP and MIME, then keep reading.
Understanding SMTP Basics
In the world of email communication, you’ll encounter SMTP, an application layer protocol that’s vital for transferring emails between servers and networks. It sets the rules for interaction between the SMTP client and the SMTP server.

Introduced way back in 1982, SMTP clients support various functions such as relaying, email queues, and alternate addresses. If you’re trying to send an attachment or a message that exceeds SMTP’s limits, MIME comes to the rescue.
An extended version of SMTP, known as ESMTP, arrived in 1995. It uses the EHLO command to initiate the connection and allows additional parameters in MAIL FROM and RCPT TO commands.
For securing SMTP, SMTPS uses TLS or SSL protocols.
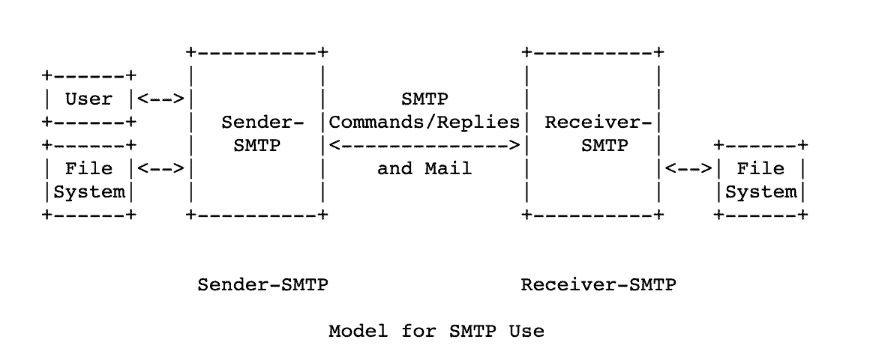
Understanding these basics helps you navigate the email communication world more efficiently.
Exploring Types of SMTP
You’ll find several types of SMTP that each play a unique role in the email communication process.
The first is the Originating SMTP servers that introduce an email into the internet.
Then there’s the Relaying SMTP servers which transmit emails between different servers without modifying the message.
Third, you have the Delivery SMTP servers that receive emails from the internet and deliver them to their final destination.
Lastly, there are Gateway SMTP servers that transfer emails between networks while transforming the message as necessary.
Each type functions to ensure that your email reaches its intended recipient securely and efficiently. So next time you hit send, you’ll know there’s more to it than meets the eye.
SMTP Infrastructure and Mail Agents
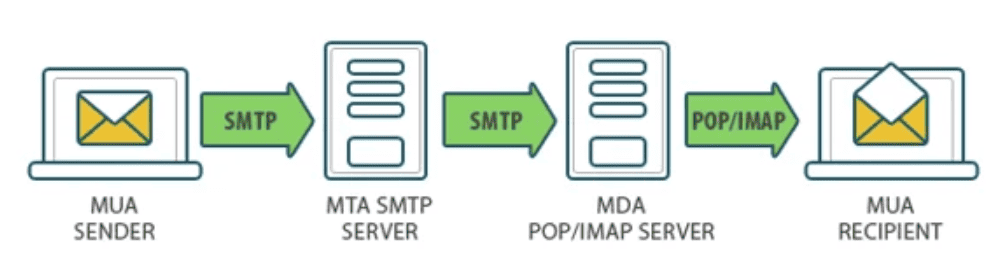
During your daily email interactions, it’s the SMTP servers and various mail agents that work behind the scenes to ensure your messages are successfully sent and received.
Essentially, an SMTP server is an application that sends emails. It can be local or cloud-based and it’s responsible for receiving messages from your email client and transferring them to their destination.
In this process, several mail agents play key roles.
- The Mail User Agent (MUA) is the email client you use to send and receive messages.
- The Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) processes and transfers emails, effectively taking on the role of a postman.
- The Mail Delivery Agent (MDA) is the last agent before delivery to the recipient’s SMTP server.
Together, these components create a robust infrastructure for email delivery.
The Role of SMTP Relay
Understanding how SMTP relay works can help you grasp the intricacies of email transmission between different SMTP servers.
In simple terms, SMTP relay is a process where an SMTP server sends an email on behalf of another server. This is especially useful when the original server can’t deliver the email directly to the recipient’s server.
To learn more about SMTP relay, consider the following points:
- It’s like a postman who transfers your mail from one post office to another until it reaches the recipient.
- It ensures that your email gets delivered even if there are issues with the direct path.
- SMTP relay servers are usually trusted servers to avoid spam.
- It’s crucial in maintaining the smooth operation of email systems.
Without the SMTP relay, email communication wouldn’t be as efficient and reliable as it is today.
SMTP and MIME – The Need for MIME in Email Messaging
What is relationship between SMTP and MIME? Now that we’ve explored the role of SMTP relay in email transmission, let’s delve into why MIME integration is crucial in modern email messaging.
Traditional email systems were designed for plain text, limiting their ability to handle diverse content types. Formatting and styling weren’t preserved, and there were restrictions on file attachments.
This is where MIME comes in.
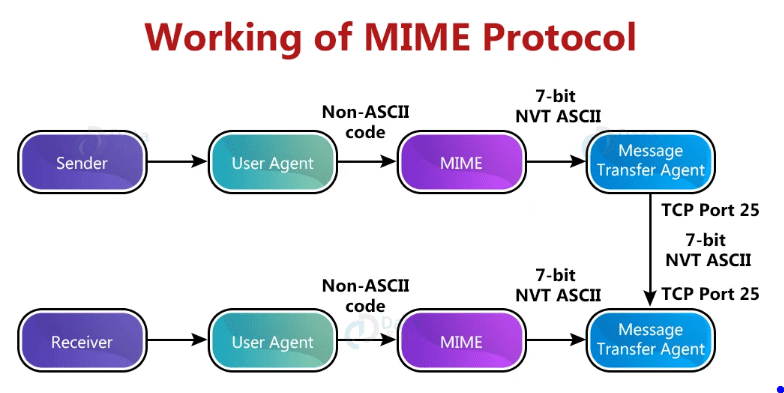
MIME, or Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions, enhances email capabilities by integrating multimedia elements and non-textual data. It ensures consistent interpretation and rendering of messages across different email clients and servers.
With MIME, you can send attachments of various formats and sizes, enhancing the visual appeal and organization of your emails.
Overcoming Limitations With MIME
How does MIME help overcome the limitations of traditional email systems? MIME, or Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions, conquers the obstacles of traditional email in numerous ways:
- Allows non-text attachments: You can send images, audio files, and even videos as part of your emails.
- Supports international character sets: Now you can compose emails in any language you want, breaking the barrier of ASCII text.
- Enables rich text emails: With MIME, you can send emails with bold, italics, and colored fonts, giving your emails a professional look.
- Handles multipart messages: You can send an email with multiple parts, each with different types of data.
What is MIME in simpler terms?
So, you’ve brushed up on how MIME overcomes traditional email limitations, but what exactly is it?
MIME, or Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions, is a way to send other types of data besides just plain text over email.
It’s a standard that ensures different email systems can all understand and display the same types of content, whether it’s audio, video, images, or non-textual data.
You know when you attach a file to an email? That’s MIME in action.
It encodes your file into a format that can be sent over email, and then the recipient’s email client decodes it back into its original format.
How MIME Works in Email Messaging
When you’re sending an email with attachments or other non-textual data, MIME is the behind-the-scenes player making it all possible. But how exactly does it work?
- MIME identifies the type of content you’re sending. Whether it’s an image, a PDF, or even an audio file, MIME labels it with the appropriate media type.
- It encodes your content into a format that can safely travel over the internet. Your attachment might start as a binary file on your computer, but MIME transforms it into text data that won’t get scrambled in transit.
- Once your email reaches its destination, MIME takes center stage again, decoding the text data back into its original form.
- MIME tells the recipient’s email client how to display the content, ensuring that your email appears just as you intended.
Last Words on SMTP and MIME
So, you’ve journeyed through the intricate world of email language, understanding SMTP and MIME – SMTP’s crucial role and MIME’s capacity for diverse content. You’ve seen how SMTPS secures your emails and explored the vital roles of MUA, MTA, and SMTP servers.
Now, armed with this knowledge, you can better appreciate the complex process that makes sending an email as simple as a click. Remember, every email you send is a testament to this fascinating tech symphony.