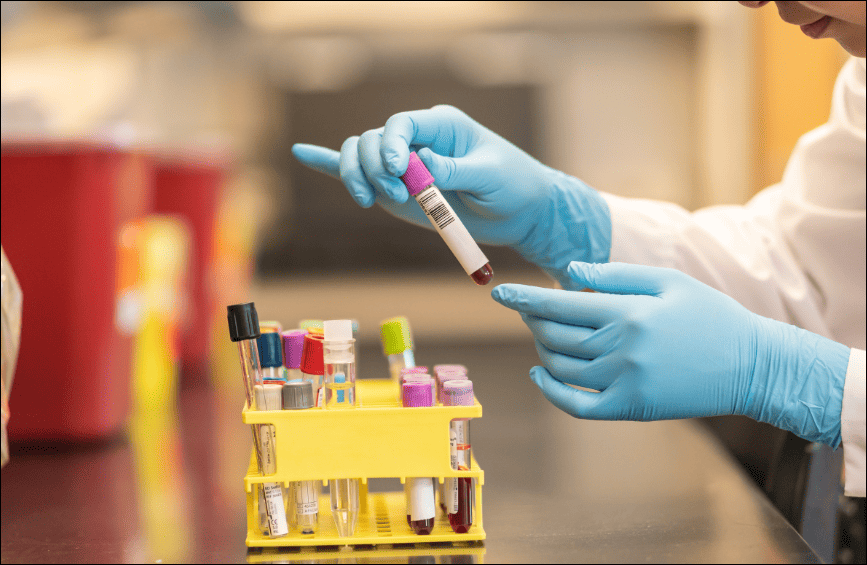
Phlebotomy, the practice of drawing blood for medical testing, transfusions, or research, is a valued and essential role within the healthcare industry. Embarking on a career as a phlebotomist offers the unique opportunity to contribute to patient care and the diagnosis process, making a real difference in people's lives.
Table of Contents
Becoming a successful phlebotomist requires several key steps that one must follow. This guide aims to outline these steps, from initial education and certification to gaining hands-on experience and honing interpersonal skills.
Whether you're just starting your career or looking to transition into the healthcare field, becoming a successful phlebotomist can be a rewarding path with numerous opportunities for growth and advancement.

Understanding the Role of a Phlebotomist
Phlebotomists are integral members of the healthcare team, tasked with the crucial responsibility of collecting blood samples from patients.
These samples are vital for a wide range of medical purposes, including diagnostic tests, transfusions, research, and disease management. The accuracy and quality of the blood draw directly impact the diagnosis and treatment plan, underlining the importance of the phlebotomist's expertise and precision.
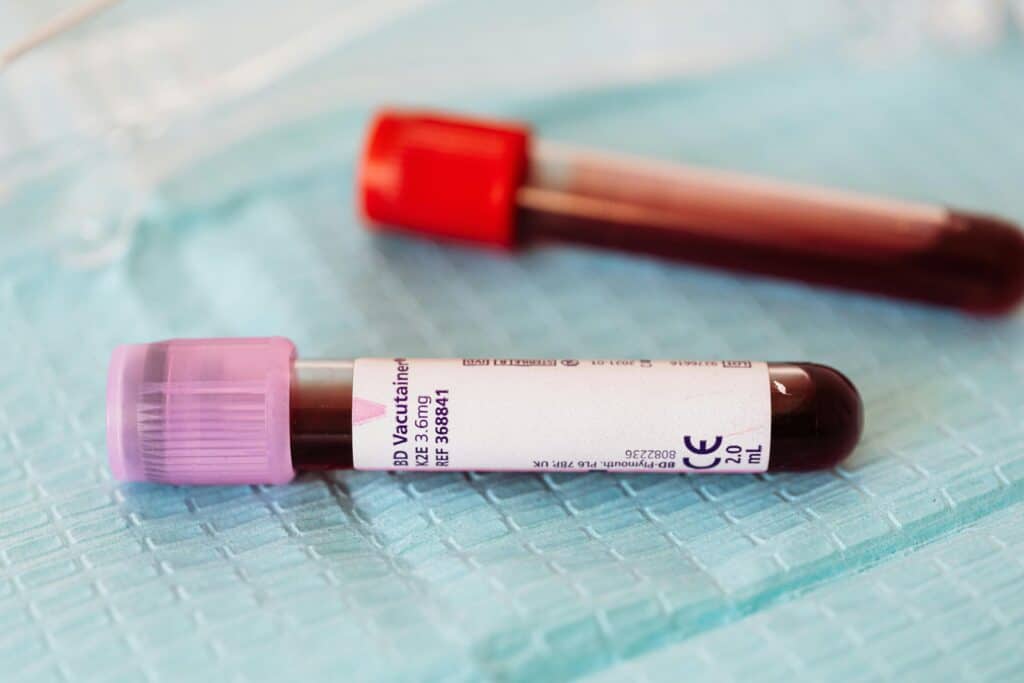
Furthermore, phlebotomists often serve as the initial point of contact between patients and the medical system, placing them in a unique position to ease patient anxieties and foster a trusting healthcare environment.
Their work directly impacts patient care and the overall efficiency of medical laboratories and hospitals. By ensuring that blood samples are collected safely, accurately, and efficiently, phlebotomists play a crucial role in the diagnostic process.
Their ability to perform under pressure, maintain meticulous attention to detail, and uphold the highest standards of cleanliness and protocol not only aids in the accurate diagnosis of patient conditions but also contributes significantly to the prevention of laboratory errors.
This directly enhances patient outcomes and trust in the healthcare system, making the role of a phlebotomist both valuable and indispensable.
Educational Requirements
To start a career in phlebotomy, candidates must first complete a phlebotomy program from an accredited institution. These programs, often offered by community colleges, vocational schools, and some hospitals, typically range from 4 to 8 months and include both classroom instruction and practical training.
If you live in NY, for example, you can look up phlebotomy training NY and find a list of accredited institutions offering programs in your area.
During this education, phlebotomy students learn about human anatomy and physiology, the circulatory system, infection control procedures, medical terminology, and laboratory techniques.
Coursework also covers the basics of phlebotomy, including venipuncture and capillary techniques, proper specimen handling and labeling, and how to interact with patients. Upon completion of a phlebotomy program, students receive a certificate of completion and are eligible to take national certification exams.
Certification Process
Achieving certification is a critical step for any aspiring phlebotomist, as it serves as a testament to their skills, knowledge, and commitment to high professional standards.
Several organizations offer certification, including the National Healthcareer Association (NHA), the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP), and the American Medical Technologists (AMT).
To obtain certification, candidates must typically pass an exam that assesses their understanding of phlebotomy techniques, safety protocols, legal considerations, and patient interaction. Preparing for this exam can involve additional study, often with materials provided by the certifying organization or through independent study courses.
After successfully passing the certification exam, phlebotomists must maintain their certification through continuing education. The field of phlebotomy, like much of healthcare, is constantly evolving with new procedures, technologies, and regulations.
Continuous learning ensures that phlebotomists stay current on best practices, thereby enhancing patient care and safety. This requirement underscores the importance of a commitment to ongoing professional development as a core component of a successful phlebotomy career.
Once certified, the next vital step is to gain hands-on experience. Entry-level positions in hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic laboratories offer valuable opportunities for newly certified phlebotomists to hone their skills.
This phase is crucial for building confidence in performing blood draws, handling specimens properly, and interacting effectively with patients and healthcare staff. Experience also allows phlebotomists to familiarize themselves with the workflow of medical laboratories and understand their role within the broader healthcare ecosystem.
Achieving proficiency through practice is indispensable for any phlebotomist aiming to excel in their career and contribute significantly to patient care and the diagnostic process.
Gaining Hands-On Experience
Gaining hands-on experience is a crucial aspect of becoming a successful phlebotomist. It not only helps hone technical skills but also allows for the development of interpersonal skills and professional relationships within the healthcare community.
This can lead to potential career advancement opportunities, including supervisory roles or specialized positions in areas such as pediatric phlebotomy or blood bank services.
Additionally, aspiring phlebotomists can expand their skillset by pursuing additional certifications in related fields such as EKG or IV therapy. This can open up new career pathways and enhance overall marketability. With the constantly evolving landscape of healthcare, having a diverse skillset can be advantageous for career growth and job security.
Developing Interpersonal Skills
Effective communication and empathy are indispensable traits for a phlebotomist. These soft skills are critical in ensuring a positive experience for patients who may feel anxious or uncomfortable about the blood draw process.
By actively listening to patients' concerns, explaining procedures clearly, and demonstrating empathy, phlebotomists can significantly ease patient anxieties. This not only facilitates a smoother process but also builds trust and rapport between the phlebotomist and the patient.
Additionally, effective communication with healthcare team members ensures accurate and efficient collaboration, further enhancing the quality of patient care. Cultivating these interpersonal skills is as crucial as technical proficiency in the pursuit of excellence in the phlebotomy field.
Understanding and mitigating patient anxiety is fundamental for phlebotomists. They frequently interact with patients who may feel anxious or fearful about having their blood drawn, a condition medically known as trypanophobia. To address this, phlebotomists employ various strategies to create a calming environment.
This includes engaging in gentle conversation to distract the patient, using a confident yet soothing tone, and being transparent about each step of the process to demystify the procedure.
By acknowledging the patient's fears and providing reassurance, phlebotomists can significantly reduce patient stress, leading to a more positive and less traumatic experience. This approach not only facilitates easier blood collection but also contributes to the overall perception of care and professionalism within the healthcare setting.
Advancement and Specialization
After gaining experience, phlebotomists can explore opportunities for advancement or specialization within the field. Advancing in phlebotomy might involve moving into supervisory or managerial roles, overseeing other phlebotomists, or managing entire laboratory departments.
Additionally, experienced phlebotomists may choose to specialize in areas such as pediatric phlebotomy, where drawing blood from children requires a particularly gentle touch and comforting approach, or in geriatric phlebotomy, focusing on the needs of elderly patients.
Another route is becoming a phlebotomy instructor, teaching new students the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in the profession. Specializing in specific areas not only enhances a phlebotomist’s skill set but also increases their value within the healthcare team, opening up new paths for career growth and personal fulfillment.
Specializing in a focused area such as blood banking presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities for phlebotomists.
In blood bank settings, phlebotomists must understand the complexities of blood typing, cross-matching, and the critical role their work plays in transfusion medicine. These specialists are tasked with not only collecting but also processing and ensuring the safety of blood donations.
Their expert knowledge in handling and storing different blood components is vital for surgeries, transfusions, and various medical treatments. Working in blood banking requires a high level of precision and a deep understanding of transfusion practices and regulations.
For phlebotomists passionate about contributing to lifesaving procedures, specializing in blood banking can be incredibly rewarding and offers a pathway to significantly impact patient care.
Continuing Education and Professional Development
The healthcare field is always evolving, making continuous learning essential for phlebotomists. Staying abreast of the latest technological advancements, safety protocols, and industry regulations is not only crucial for providing the highest quality patient care but also for personal career development.
Many professional organizations and educational institutions offer seminars, workshops, and online courses specifically designed for phlebotomists seeking to enhance their knowledge and skills. Engaging in these educational opportunities can fulfill the continuing education requirements necessary for maintaining certification.
By prioritizing professional development, phlebotomists can ensure they remain competitive in the job market, ready to tackle new challenges, and capable of delivering care that meets the dynamic needs of the healthcare sector.
Attending workshops, conferences, and courses can keep professionals updated on the latest practices and technologies, further enhancing their capabilities in the field.
These gatherings serve not only as platforms for learning new skills but also as opportunities to network with peers and industry leaders. For phlebotomists, such events can be invaluable in uncovering evolving trends in blood collection technology, safety measures, and patient care techniques. ,

In conclusion, the role of a phlebotomist is both challenging and immensely valuable within the healthcare industry.
From the meticulous collection of blood samples that form the basis of diagnostic procedures to the comforting presence, they offer patients during potentially stressful moments, phlebotomists significantly contribute to patient care and the efficacy of medical treatments.
Their dedication to continual learning and professional development ensures that they remain at the forefront of advancements in healthcare practices, further elevating the standard of patient care.
Becoming a Successful Phlebotomist – FAQs
1. How long does it typically take to become a certified phlebotomist?
It typically takes anywhere from 4 to 8 months to complete a phlebotomy program, which includes classroom instruction and hands-on training. After completing a program, candidates must then pass a certification exam.
The timeframe for becoming a certified phlebotomist can vary based on the individual's study pace for the certification exam and the scheduling of the exam itself.
2. Is certification necessary for becoming a successful phlebotomist in all states?
Certification requirements for becoming a successful phlebotomist can vary significantly from state to state.
While some states do require phlebotomists to be certified, others may not have specific certification requirements but still prefer or require completion of a phlebotomy program. It's important to check the regulations of the specific state where you plan to practice.
3. Can phlebotomists advance in their careers?
Yes, experienced phlebotomists have various avenues for career advancement and specialization.
They can move into supervisory or managerial roles, specialize in areas such as pediatric or geriatric phlebotomy, or become instructors in phlebotomy programs. Additional certifications in related fields, like EKG or IV therapy, can also open up new career paths.
4. What are the most important skills for becoming a successful phlebotomist?
Important skills for becoming a successful phlebotomist include technical proficiency in drawing blood, a thorough understanding of safety protocols and infection control, and excellent communication skills.
Additionally, traits like empathy, patience, and the ability to work under pressure are crucial for providing patient comfort and ensuring a positive experience.
5. How can a phlebotomist maintain their certification?
Phlebotomists maintain their certification through continuing education.
This involves completing a certain number of hours in continuing education courses, workshops, or seminars within a specific timeframe, as required by the certifying organization. Continuous learning helps phlebotomists stay updated on the latest practices, technologies, and regulatory changes in the healthcare industry.